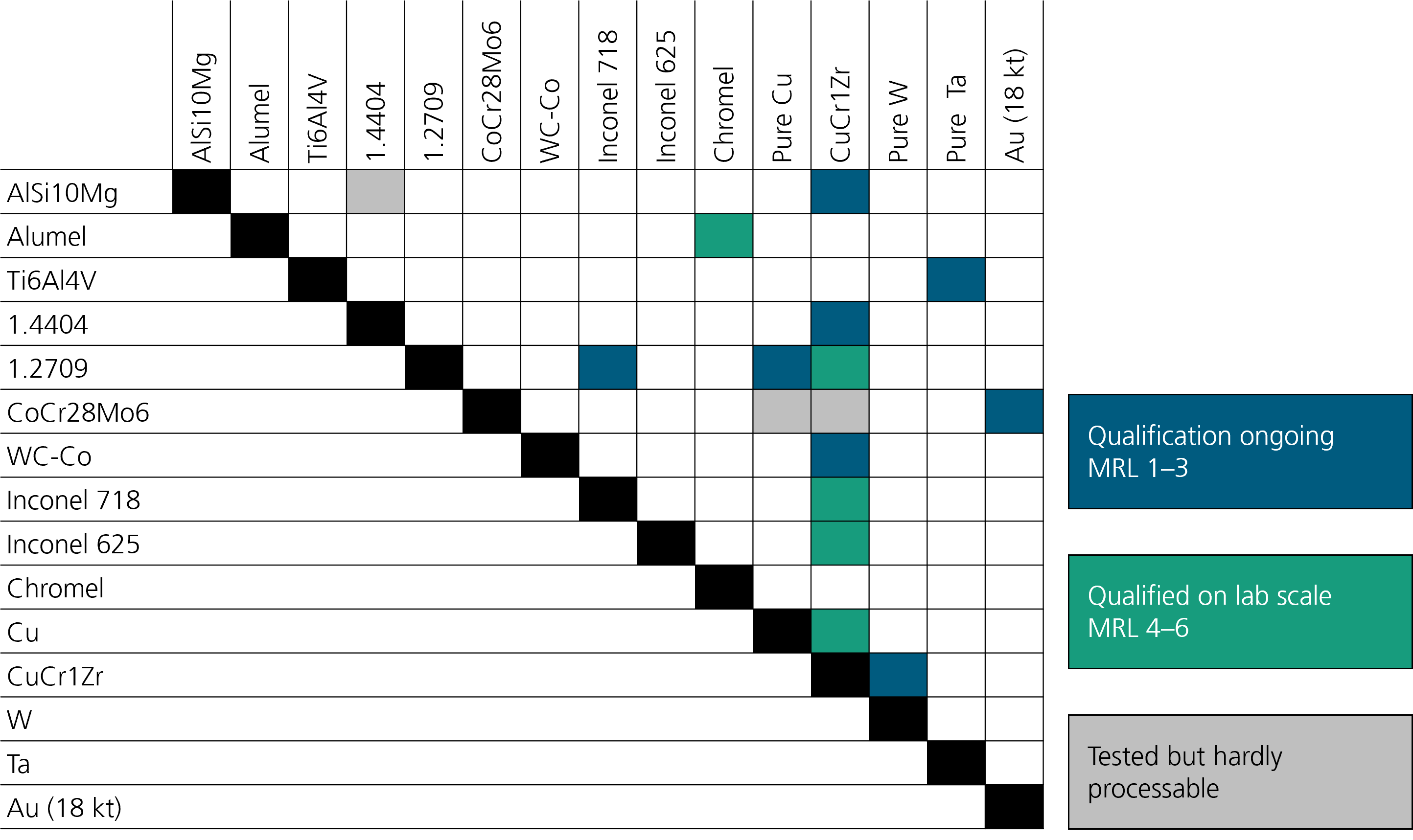
Additive manufacturing is constantly evolving and the call for larger components, higher production speeds and more cost-effective processes in particular is becoming ever louder. We at the Fraunhofer IGCV are also taking this into account and are working on a number of emerging technologies.
Hybrid construction methods
When using hybrid construction methods, additive manufacturing is only used to produce the part of the component on which the manufacturing technology can also achieve added value. For this purpose, a base body is produced using a favorable manufacturing process, positioned and aligned in an AM machine so that the complex part of the component is applied to the base body with high positioning accuracy. Our Autohybrid project is researching this manufacturing option in more detail.
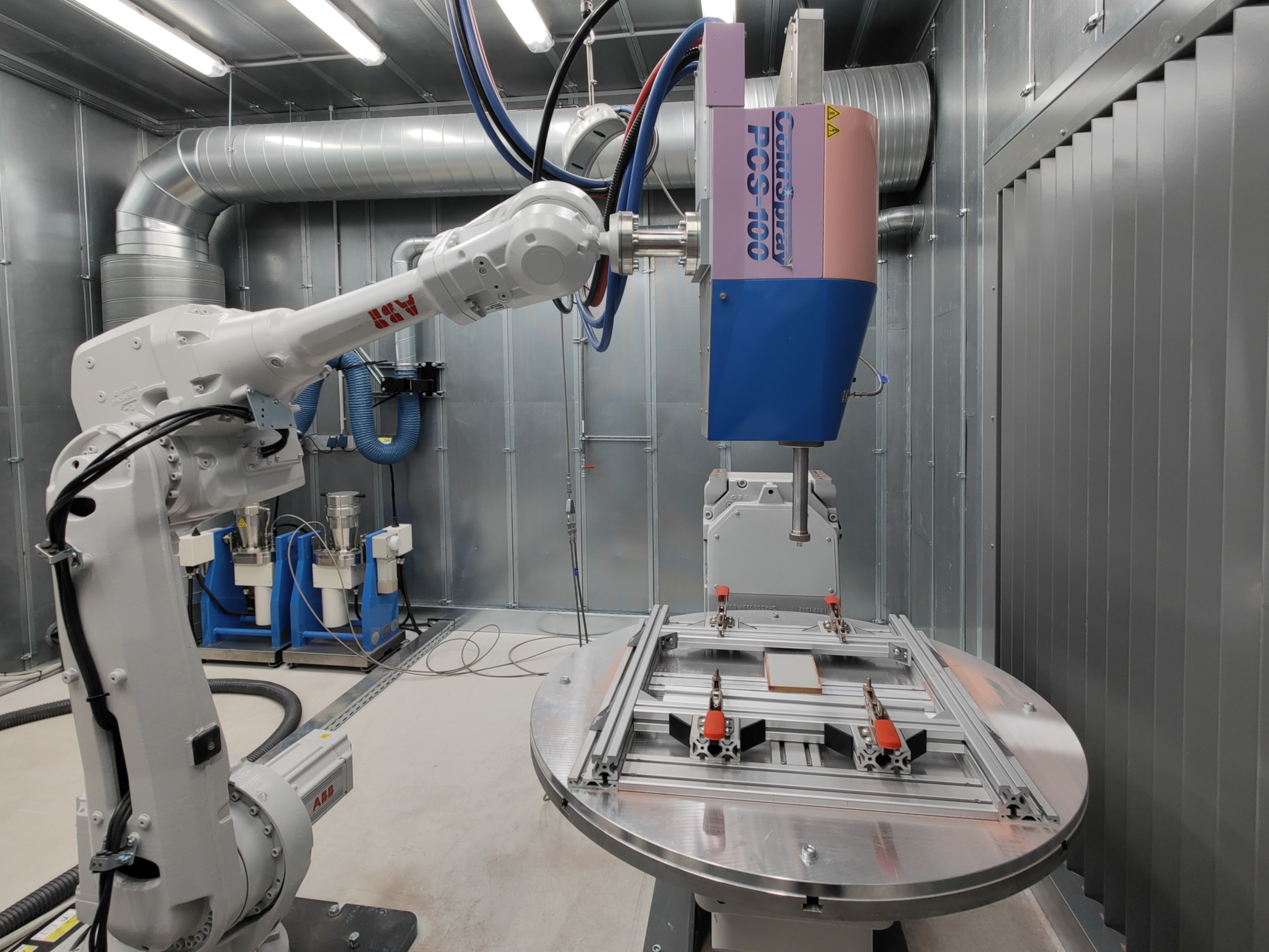
High-pressure cold gas spraying
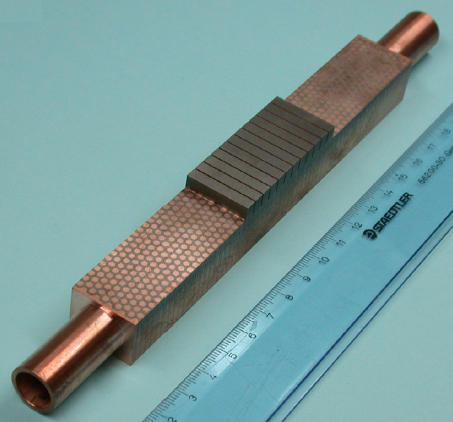
In the area of large components, we have opted for the further development of high-pressure cold gas spraying towards additive manufacturing technology. The process enables very high application rates (up to 10 kg/h) and materials can be combined that are very difficult to join using welding processes, for example. The FASTMULT, Coldspraymult and ACCURACY projects are developing the basic principles for this.
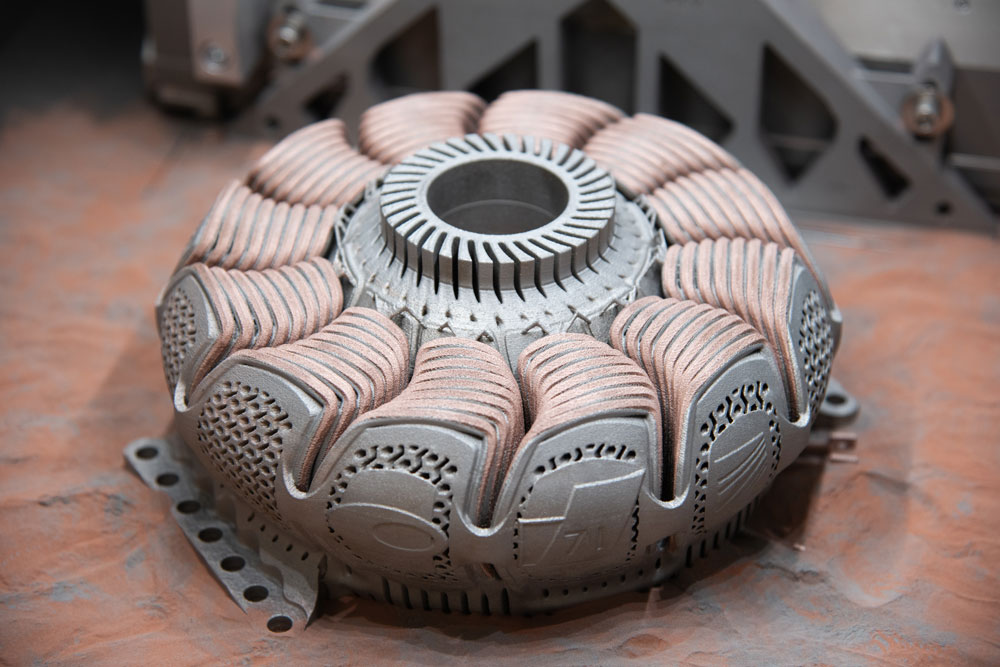
Powder Bed Fusion of Metals using a Laser Beam (PBF-LB/M)
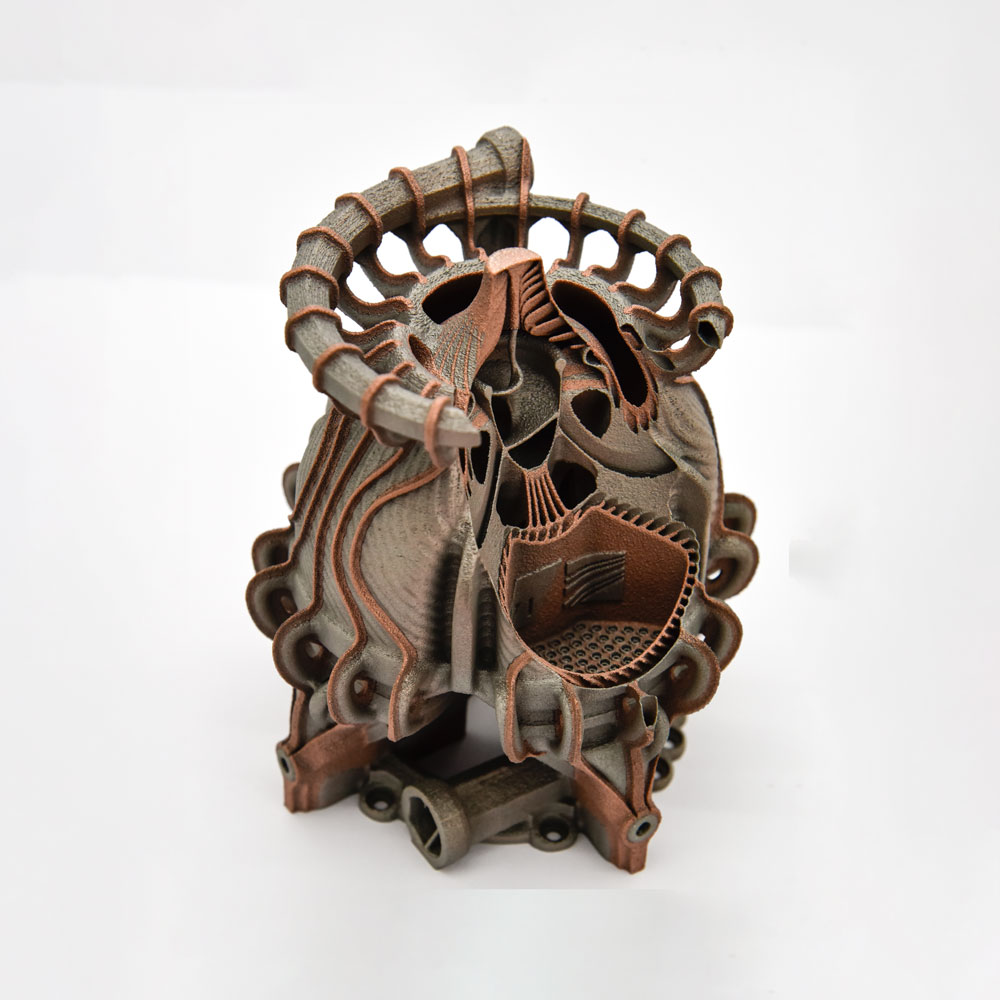
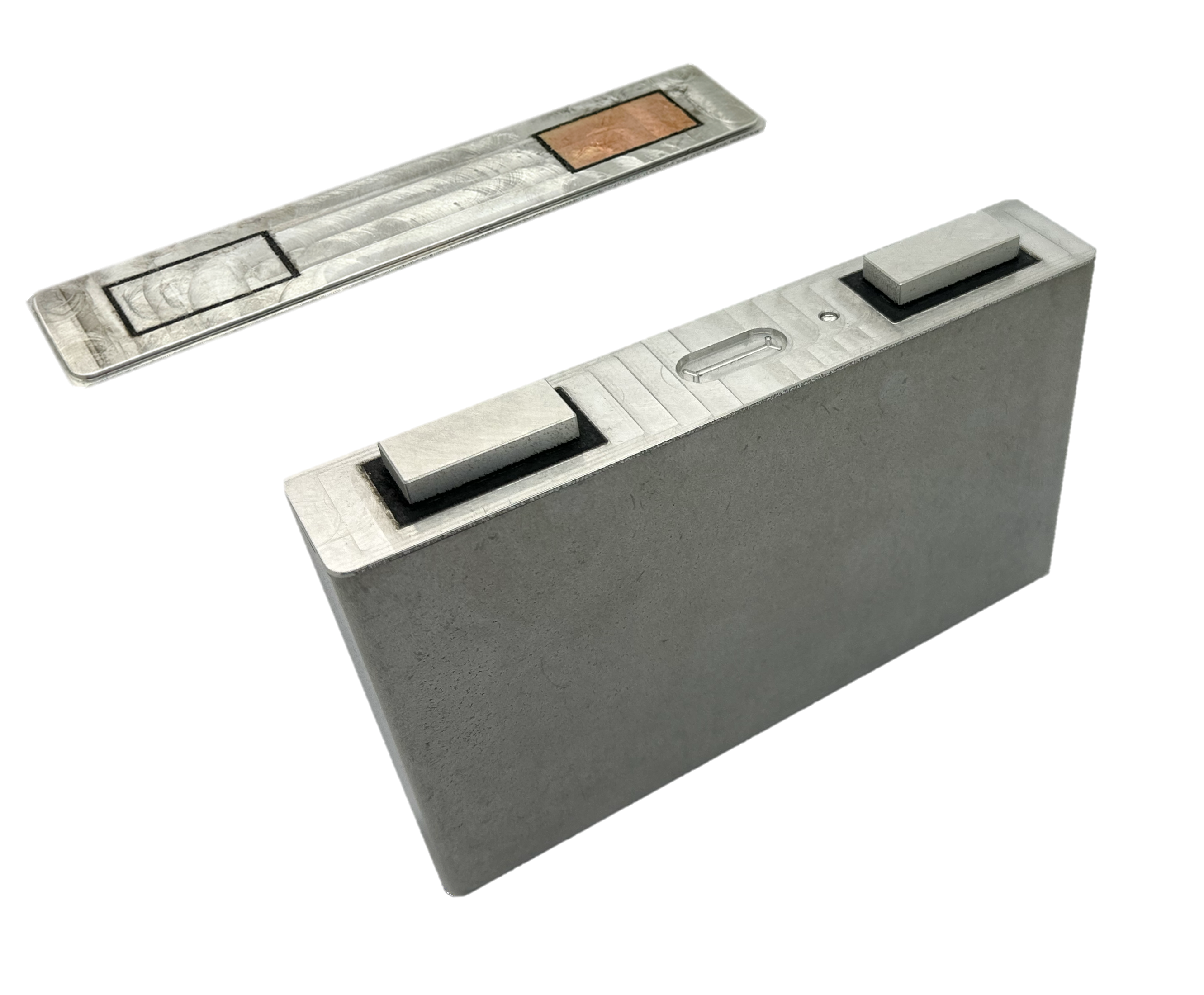
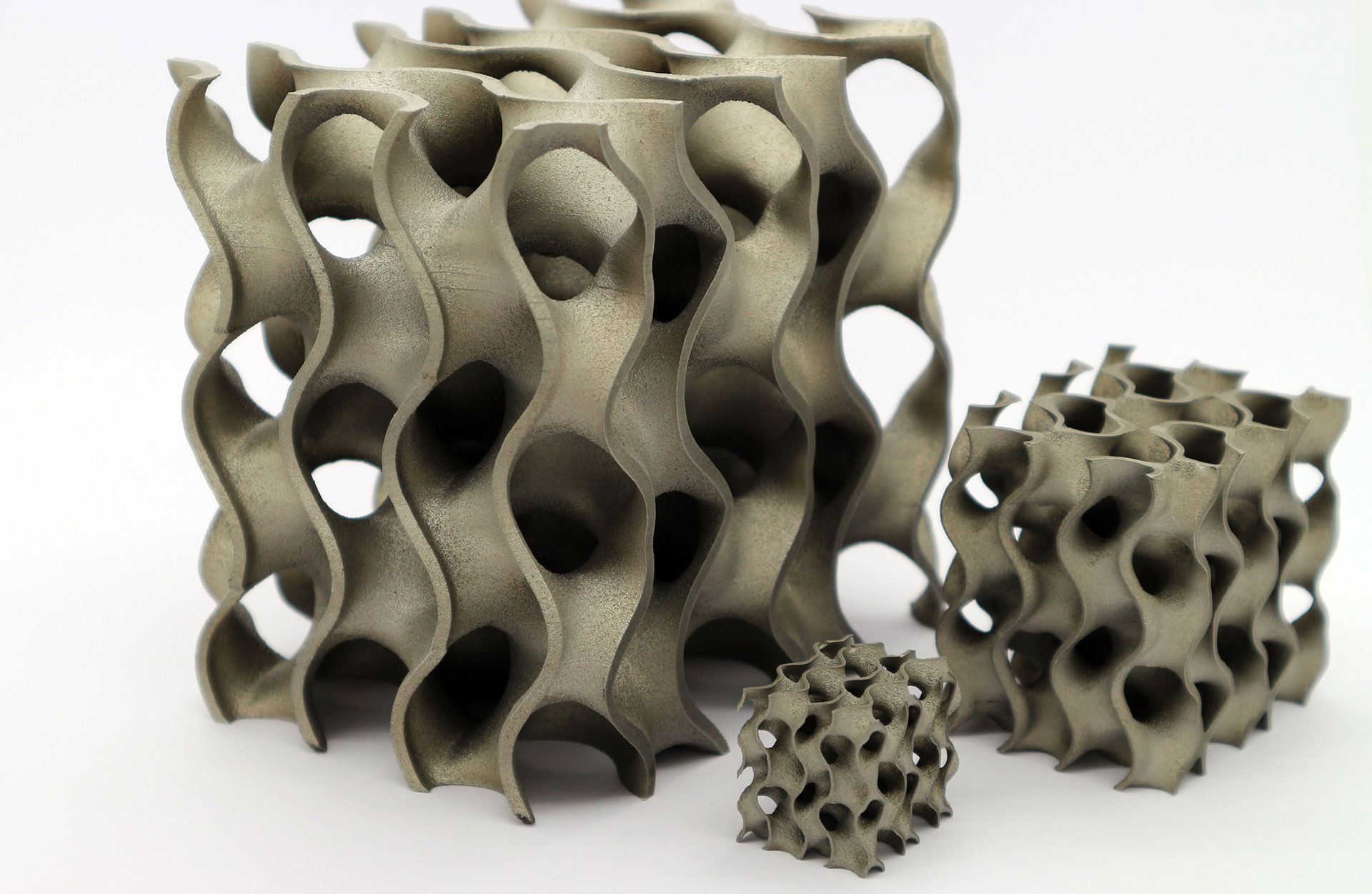
The materials used must be available in fine powder form to apply a thin layer to the build platform. A powerful laser then selectively melts the powder (laser-based powder bed fusion, LPBF). The locations at which the powder is exposed can be determined directly from the CAD data of the component to be produced. This makes it possible to realize the most complex structures without tools, achieving maximum stability with low weight. Besides, a new form of functional integration is possible. For example, cavities can be left free during the building process to integrate sensor technology into solid material components. In this way, information can be collected in components at points otherwise difficult or impossible to reach.
Liquid metal printing
One of the latest processes in our laboratory is liquid metal printing (LMP), which is being further developed in our AluWire LMP project together with Grob. In this process, molten metal is produced in a small crucible and liquid droplets are deposited to create the component. An aluminum wire is used as the raw material. Especially for the processing of aluminum alloys, production costs and production times can be significantly reduced compared to other additive manufacturing processes.
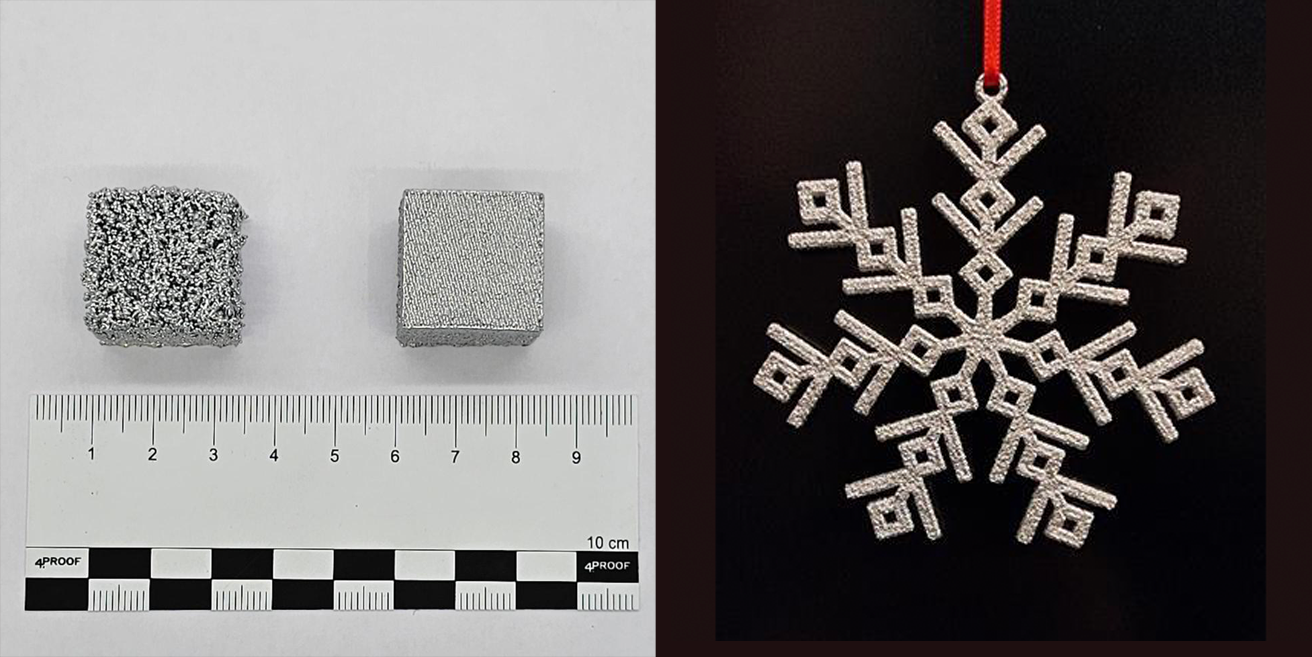
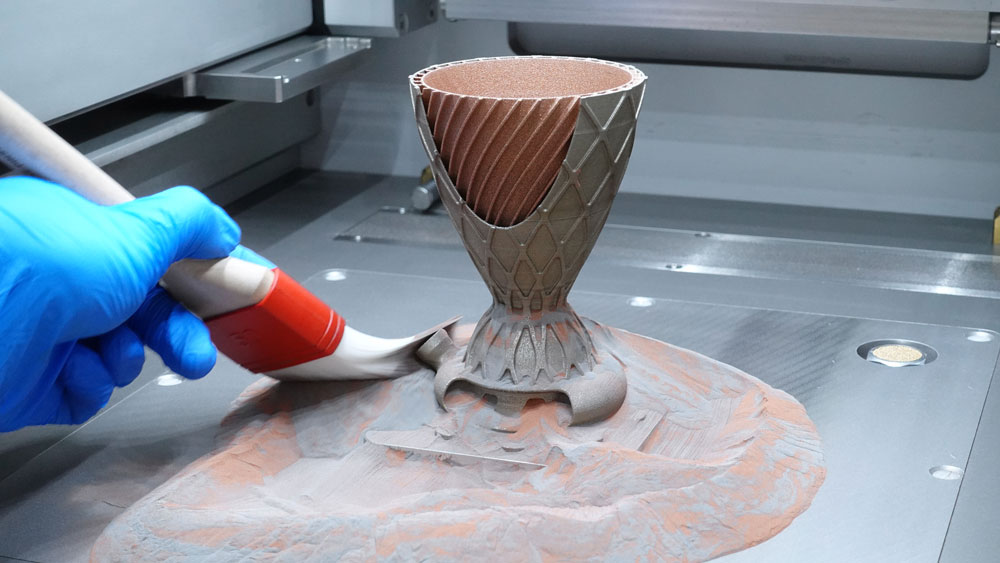
Metal Binder Jetting
As a sinter-based AM technology, metal binder jetting is particularly suitable for the production of small components in large quantities. The sintering process also allows materials to be processed that cannot be processed using melting or welding-based methods. The focus in this area is on steels and hard metals.