Exploit synergies from multiple additive manufacturing technologies
In industry today, the focus is on energy-efficient and resource-saving component design. It so happens that lightweight construction is enjoying growing attention.
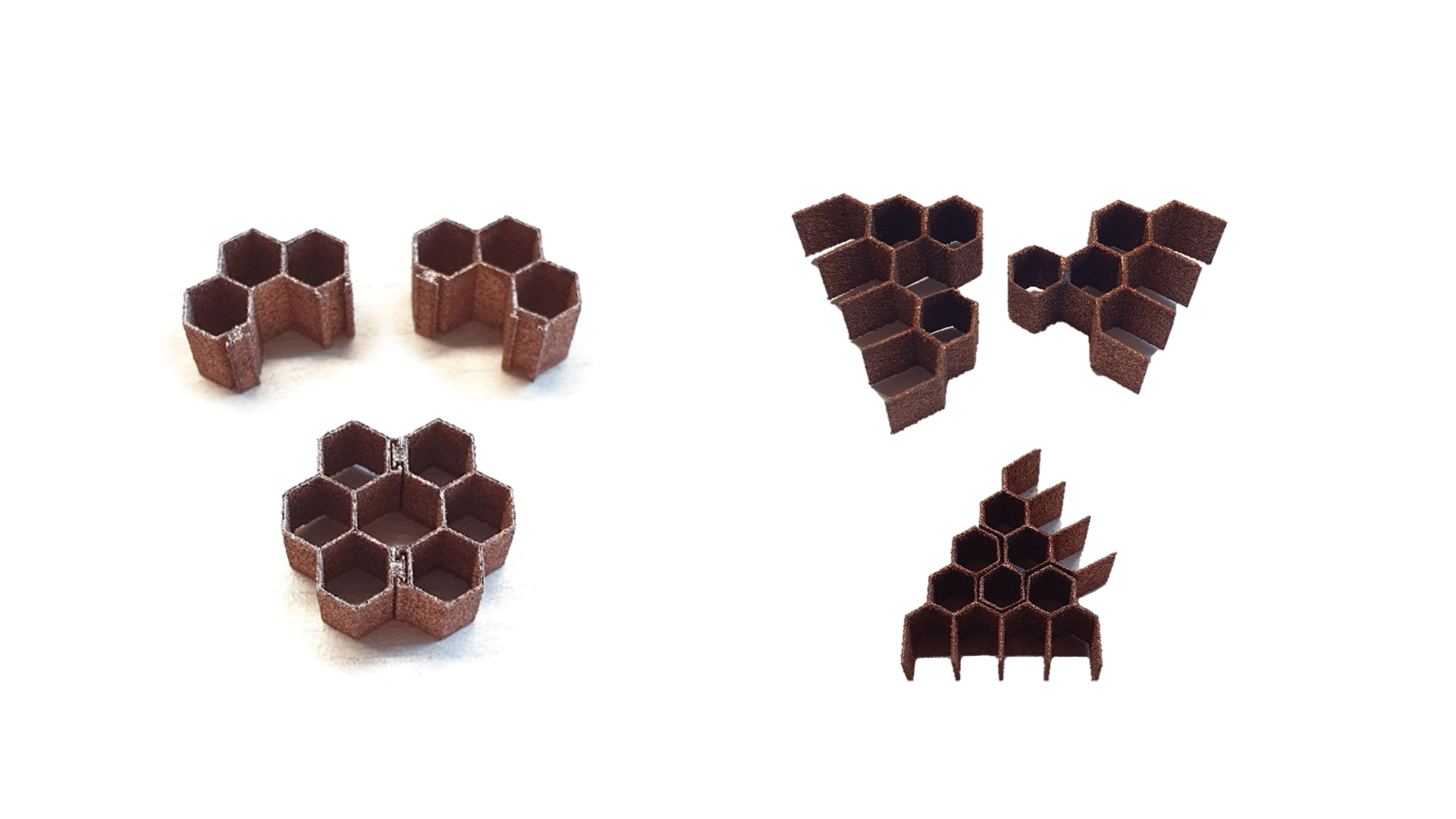
Sandwich composites are well-known lightweight structures used in aerospace wings and rotors, satellite structures in space travel, rotor blades of wind turbines, or in many areas of automotive engineering. A sandwich composite comprises a low-density core and two thin, highly rigid outer layers. According to the current state of the art, the components are manufactured separately and then bonded together.
The use of sandwich structures has been limited in that curved surfaces can only be reproduced with difficulty by the shape-giving core structure. In addition, the subsequent forming of the sandwich composite quickly leads to debonding between the cover layers and the core.
The aim of the "MC-Sandwich" project is, therefore, to develop hybrid process chains for the production of innovative, highly complex sandwich structures using a metal-fiber composite approach. This will shorten the complex production chain for sandwich composites and thus enable the cost-effective production of lightweight structures.